Εμφάνιση αναρτήσεων με ετικέτα Έρευνα για την Άσκηση. Εμφάνιση όλων των αναρτήσεων
Εμφάνιση αναρτήσεων με ετικέτα Έρευνα για την Άσκηση. Εμφάνιση όλων των αναρτήσεων
Τετάρτη 20 Οκτωβρίου 2021
Τετάρτη 8 Ιουλίου 2020
HIIT Training : Long Intensive Runs or Short Intensive Runs?
Posted by
paulgotsis
at
6:44 μ.μ.
High Intensity Intermittent-Interval Training
Like I Think of It I Use It I Analyze ...
Tips Directions, Examples of Professional and Amateur Football in the new
Μagazine "MR-FOOTBALL" to be released ..
An excellent article very useful for the Pre Season Period .
I avoid talking about generalities in this article, I give examples from trainings that I use and always with data from the GPS.I give advices on Short and Long Interval training and we suggest for the first time in the world literature what is the best method between the two.Don't miss the next magazine of
Σάββατο 20 Οκτωβρίου 2018
HIITraining in Soccer Sample (10) Potenza Metabolica (Metabolic Power Training)
Posted by
paulgotsis
at
3:30 μ.μ.
Integrated Exercise ( Esercitazione Integrata )
Aerobic Exercise, (circuit + 3v3 + Technique + Possession) and Maximal Run 25m
Video -Animation
Divide the team into 2 groups and position them diagonally to the training field.
At the end of the time, the groups turn anti-clockwise.
At the bottom left is the coordinating circuit, the players will have to run the ladder, a wide lateral slalom, ladder changing exercise and finally jumping on foot joined inside the hoops + fast run at the end to start again .
Turning counter-clockwise we find the 3Vs3.
In this station you enter all the variants that are most congenial to you (touches, everyone must touch the ball etc.)
In the next one we find ourselves in the technical station, in this position the boys are positioned in cascade and perform analytical exercises of dribbling and pass.
In the last we find a simple possession of the ball. Also in this case you insert some variants if you need them.
Important:
In passing from one station and another, the players must make a length of at least 25 meters.
4-5 sets of 5 'each (45' 'work + maximum run for change exercise 25m + 1-2' rest)
Παρασκευή 14 Σεπτεμβρίου 2018
HITraining in Soccer SSGs v MSGs v LSGs Scientific Approach
Posted by
paulgotsis
at
11:16 μ.μ.
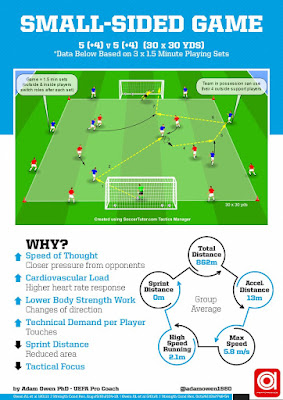
Physical and Technical Comparisons between Various Sided - Games within Professional Soccer
This study compared the technical activity and
physical moments on various sided-games within Professional Soccer.10
elite male players from a Scottish Premier League performed small- SSGs
(4v4) medium-MSGs (5v5 to 8v8 ) and large- LSGs ( 9v9 to 11v11) each
lasting for 3x5'min .Results show significant physical differences between
SSGs, MSGs and LSGs for most of the variables measured. It was shown that SSGs
induce a significantly faster playing speed when compared to MSGs and LSGs
(150.5 vs 108.3 vs 120.4 m.min but significantly less repeated high -
intensity efforts (0.88 vs 4.40m) high -intensity running(7
vs 39m ) and sprint distance (0 vs 11m) when compared to LSGs .Findings
also revealed significant differences between SSGs ,MSGs and LSGs in
technical demands (passes,dribbles,shotsheaders ).High levels of
reproducibility (ICC=0.99) where yielded when using the same sided-games to
facilitate its use as part a periodised weekly structure.
At the Elite level of the sport ,players are suggested to need a high
level of aerobic endurance involving lower sub-maximal intensities
coupled with an ability to reproduce high-intensity ,maximal efforts .Previous
research has indicated that SSGs induce significantly higher HR responses
as compared to LSGs allowing for an aerobic development .Furthermore
during SSGs players spent significantly longer time in the >85% maximal
HR zone (large effect ) as compared to large sided games. When
discussing the speed or intensity of play within this study it should be
noted how the meters (m.min ) between the sided games where significantly
different with SSGs showing the highest meters values(198.5mmin )when compared
to MSGs (106.9 m.min ) and LSGs (120.4 m.min ).The faster speed of play within
the SSGs may be associated with the smaller pitch size and limited time in
possession of the ball due to close proximity of the opponents.The results show
that as the number of players increase from SSGs ,MSGs,to LSGs the speed of
play decreases due to less pressure from the opponents increased
pitch sizes and more passing options ensuring the players can limit the
amount of running they perform. However, SSGs and MSGs do not induce high-speed
movements when compared to LSGs.
Key Point 1 (Pitch Size - Ball Contacts) :
Key Point 2 (Passing):The investigation revealed a significant difference between each game (SSGs,MSGs,LSGs)
with respect to number of passes. The results show that the more players
on the pitch ,the fewer total passes made. This may be attributed to the fact
that when there are fewer players on the pitch (4v4 to 11v11)the pitch
dimensions are smaller and coincidentally the are less passing options ,coupled
with the fact that there is more pressure applied on the person in possession
of the ball ,increasing the need to pass more.
Key Point 3 (Dribbling) :More dribbling in SSGs when
compared to MSGs and LSGs.Due to their being less passing options within the
SSGs ,the increased need for players to dribble past opponents to create space
in trying to maintain possession is a key function of these type of games. According
to (Hoff ),when dribbling the ball the energy cost is significantly higher
pushing HR responses within SSGs higher.
Key Point 4 (Microcycle) : The combination of different sided games throughout the course of
training week is something that should be noted in order to maximize the preparation
of the players and expose players to varying physical and technical demands
within a more controlled environment.
Sample 1 ( SSG )
Sample 2 ( LSG )
Authors : Adam l Owen ,Darren J Paul ,Del P .Wong ,Dellal A
"Physical and Technical Comparisons between Various Sided Games within Professional Soccer "
https://www.researchgate.net/publication/256490435_Physical_and_Technical_Comparisons_between_Various-Sided_Games_within_Professional_Soccer
Δευτέρα 27 Αυγούστου 2018
HIITraining in Soccer Sample (6) Potenza Aerobica (Metabolic Power Training)
Posted by
paulgotsis
at
4:30 μ.μ.
High Intensity Training Programme 1

Speed Endurance : 5 Laps 2'min each lap
The Running Speed is expressed as a % of the maximum speed.
Set :2 Laps :5 Rest Set :3'min All together 10'+3'+10=23'min
The one side is between 90-100m the other side 60m
High Intensity Training Programme 2
High Intensity Training : 1 lap 1.05'' 10-12 laps
From the start run at High Intensity to the other side of the field
turn around the cone and return at High Intensity (150m=30''sec)
as indicated in the picture ,afterwards walk or slow jog to the Starting P
(50m=35''sec ) and repeat 5-6 laps or 10-12 Repetitions.
Total Duration:21'.40'' Total Distance :4000m
High Intensity Training Programme 3
This High Intensity Running is in Anaerobic Lactic Threshold Zone
The Professional Soccer Players range between (88-92% FCmax the Anaerobic Threshold Zone the lower threshold range between 85-88% FCmax ).The players who have lower AT we put them to run in this zone between 85-88% but in the faster parts of this Physical Circuit in 2' and 1' they will run into 90-92% FCmax about 6-10 bouts upper threshold.
Αll these programs I chose because they are suitable to quickly prepare some players who came late in the team very near to the start of official duties or to keep during the year the players who are out of the list in the official games.
(Werner.Helsen UEFA Referees Committe ,2017-18) Performance Training in Football Refereeing

Speed Endurance : 5 Laps 2'min each lap
The Running Speed is expressed as a % of the maximum speed.
Set :2 Laps :5 Rest Set :3'min All together 10'+3'+10=23'min
The one side is between 90-100m the other side 60m
High Intensity Training Programme 2
High Intensity Training : 1 lap 1.05'' 10-12 laps
From the start run at High Intensity to the other side of the field
turn around the cone and return at High Intensity (150m=30''sec)
as indicated in the picture ,afterwards walk or slow jog to the Starting P
(50m=35''sec ) and repeat 5-6 laps or 10-12 Repetitions.
Total Duration:21'.40'' Total Distance :4000m
High Intensity Training Programme 3
This High Intensity Running is in Anaerobic Lactic Threshold Zone
The Professional Soccer Players range between (88-92% FCmax the Anaerobic Threshold Zone the lower threshold range between 85-88% FCmax ).The players who have lower AT we put them to run in this zone between 85-88% but in the faster parts of this Physical Circuit in 2' and 1' they will run into 90-92% FCmax about 6-10 bouts upper threshold.
Αll these programs I chose because they are suitable to quickly prepare some players who came late in the team very near to the start of official duties or to keep during the year the players who are out of the list in the official games.
(Werner.Helsen UEFA Referees Committe ,2017-18) Performance Training in Football Refereeing
Δευτέρα 9 Ιουλίου 2018
HIITraining in Soccer Sample (3) Potenza Aerobica (Metabolic Power Training)
Posted by
paulgotsis
at
11:52 μ.μ.
Aerobic High Intensity Training with Technical Skills
We present the aerobic-anaerobic high intensity training :
15''-30''High Intensity Intermittent Training : 15'' Work Box to Box :72-75m Rest:Active Recovery Technical skills passing on pairs .In this video the author propose distance 80m in 15'' with active recovery 30'' ,8-10 repetitions Duration:6-7'min 2-4 Set .Rest Set :2-3'min .
15''-45'' High Intensity Intermittent Training : Run at high intensity more tha 18km/h from center circle to corner flag and return in 16'' the distance covered is 100 yard (91m) and the recovery in the circle is 44'', harte-rate is between (155-170b/1') .The players wears GPS monitors and we individualized the pace based the aerobic fitness level . (Both and in the 2 exercises you can adjust this distance depend the vVo2max of yours players e.x different distance for the player who has 17km/h vVo2max different distance for the player has 18km/h with this ways you can seperate the team in groups depend the vVo2max ).
These methods can be followed in the Second or Third
week in the Preparation Period .For a team that the
players are a long time with,I propose to make from
the second week this kind of training.
the desired metabolic and /or neuromascular load of the HIT
sessions with Short or Long Intervals .
All the Scientific approaches conclude that the
active recovery ,engage more the anaerobic mechanism
The most recently searches conclude that the best way
to improve the Vo2max and the anaerobic lactic acid
mechanism is ti use Long intervals especialy 2'min
92%vVo2max with 1'min Rec and 1'min 100%vVo2max
with 30'' rec and Short Intervals 20''-20'' ,15''-15'',10''-10''
15''-30'' ,15''-45'',10''-20'' 105-120%vVo2max .
Βibliography : Bucheit -Laursen "High-Intensity Interval Training ,Solutions
to the Programming Puzzle "
Yann Le Meur "French Institute of Sport ,Paris,France
Jornadas de actualizacion en rendimento deportivo Vittoria-Gasteiz
12th September 2015
Τετάρτη 20 Ιουνίου 2018
HIITraining in Soccer Sample (2) Potenza Aerobica (Metabolic Power Training)
Posted by
paulgotsis
at
6:05 μ.μ.
Specific endurance: Intermittent work and SSG in alternating reduced spaces
Specific resistance: intermittent work and games in alternating reduced spaces
What I propose to you today is a job we did at the beginning of November this year. The aim is to solicit the "specific resistance", ie the ability to sustain "repeatedly" high - intensity jobs.
First we divide the team into 2 groups that, alternatively, will perform the 2 proposals, one to "dry" and one through the use of the ball, which I will go to offer you.
The first proposal consists in performing an intermittent work 15 "- 15" on a 24mt shuttle run. Specifically, our players will have to perform in 15 "3 times the 24m or 72mt in 15" and then recover "passively" for another 15 ".
The second proposal consists in performing the exercises of 3 vs 3 or 4 vs 4 (depending on the players present) in a 30m x 30m space with a goal defended by the goalkeeper. The attacking team will have the task to make a goal in the goal defended by the goalkeeper while the team that defends, as soon as it recovers the ball, will have the goal to exceed the goal line behind the attackers having the opportunity to exploit the numerical superiority 5 vs 4 thanks to the goalkeeper.
As already explained at the beginning of the article, the work we performed consists in alternating the groups in the 2 proposals by performing 2 'of work and 2' of recovery. So a series is completed when the 2 groups have performed the 2 proposals. We have performed 3 complete series for a total of 24 'of work.
I noticed that in the last series the guys were really "tired" and struggled to maintain a high rhythm in the proposal with the ball. In this case I think it is preferable maybe at the end of the 2 series to give 30 "more recovery to keep up the pace.
Article :Resistenza Specifica :lavoro intermittente e partite in spazi ridotti alternati.
Preparatore Atletico ,Marco Benetton www.marcobenetton.wordpress.com
Date:13.11.2017
Κυριακή 3 Ιουνίου 2018
HIIT (High Intensity Intermittent Training in Soccer )
Posted by
paulgotsis
at
2:17 μ.μ.
HIT Training in High Intensity
As part of the training methodology applied to football, in recent years we hear more and more talk about high intensity training. This type of training is known in the literature as HIT (High Intensity Training) and has important supporting scientific fundamentals (Helgerud, 2007, Iaia 2008 Thomassen, 2010, Buccheit 2013).The classifications described by the authors are different, but the one that can be considered exemplary and represented in figure 1.
Long Intervals > 45'',Short Intervals < 45'',Sprint Interval Training 20-30'',R.S.A < 10"

Beyond the theoretical classifications, for teaching purposes, to program a HIT training it is necessary to manipulate nine variables (Buccheit, 2013), for which the six indicated in figure 2 are relevant for practical purposes.
a.Repetition duration b.Repetitions Intensity c.Recovery duration d.Recovery methods e.Number of Repetitions f.Number of Series
1.Long Intervals
Repetition duration: Must allow to reach the VO2max .It is recommended a duration of more than 2-3 '.
Intensity :90-95%fcmax or 90%VAM.
Recovery method :Active or Passive
Recovery duration:Greater than or equal to 3 'between repetitions
Number of Repetitions :The minimum to obtain an improvement and 4 repetitions in the case of a 4' work duration, while a greater number of repetitions occurs if the duration is shorter.
Number of Series :This type of work, providing long intervals and active recovery, allows to carry out only one series (or 2 if the duration is less than 4 minutes) to obtain positive effects.
Practical Example :4x4'min ( or 4x1000m) .This work involves several physiological parameters, in particular the VO2max. By following and monitoring the parameters described, physiological responses and performance improvements can be obtained independently if such a proposal is carried out dry or with a ball, especially in young players.(Impellizzeri ,2006 Hill-Haas ,2009)
2.Short intervals
Repetition duration: 10''-45''
Intensity :100-140% VAM The use of percentage values of the fc max in case of short intervals (above all equal to or less than 30 '') and less reliable because it does not follow the actual intensity of the training .(Billat ,2001 Laursen ,2002)
Recovery method :It can be active or passive. This last, with a fixed and intense interval, increases the lactic acid contribution. The former, on the other hand, maximizes the time spent at the Vo2max and consequently has a greater effectiveness in looking for adaptations to the aerobic system. in the use of the classic intermittent 10''-10'',15''-15'',30''-30'' only in this last active recovery increases the time spent on VO2max.
Recovery duration:Between repetitions it is equal to the duration of the interval to keep the performance fairly constant, or less than this to increase the total intensity of the exercise and "accumulate fatigue" (which is convenient to create physiological adaptations in the recovery phase of the following days). Between the series it is appropriate a recovery of 4-5 'active or of a shorter duration if passive.
Number of Repetitions/Series :is indicated what allows the right volume of training suggested by the evidence for team sports such as football, or 5-7 'of effective work.Practical Example : 2 Serie 20 repetitions 20''-20''
3.Sprint Interval Training
Repetition duration: Between 20-30''
4.Repetead Sprint Training
Repetition duration: 3-10''
Number of Series : 2-3
Practical Example : 3 Set x10 (5'') all out with change direction 90*with passive rest 25'' between repetitions 3-4'min between set.
The parameters to be considered
Intensity :all -out, or at the highest possible speed in each interval.
Recovery method : Passive to maintain constant the performance of sprint
Recovery duration:Greater than or equal to three times the duration of the sprint (always manage it based on the acute and chronic physiological response sought)
Number of Repetitions/Series :8-12
Number of Series :A single series given very high intensity is enough in this type of intervention. A valid alternative could be to use the fail method or to carry out repeated sprints until it significantly decreases the intensity for 2 consecutive sprints (for example, if you can no longer cover a certain distance), all repeated for 2-3 series, interspersed with an active recovery (at a very mild pace) of 3-4 minutes depending on the performance level of the athletes, or of a shorter duration if passive.
Practical Example : It could be the execution of 8 repetitions of 30 '' all out with a passive recovery of 90 '' Or with the fail method, one could propose 2 series of 20 '' all out with a passive recovery of 2 'between the repetitions and 2-3 'between the series.
4.Repetead Sprint Training
Repetition duration: 3-10''
Intensity : all -out
Recovery method :Active or passive based on the physiological response sought and the objectives of the training (in the same way as explained for the other types).
Recovery duration:Between the repetitions 20-60''bearing in mind that less recovery results in more time spent on the VO2max. Between the series and fundamental a large recovery, of 3-4 'if passive or up to 6 if it is active at low intensity
Number of Repetitions/Series : Greater than or equal to 6Number of Series : 2-3
Practical Example : 3 Set x10 (5'') all out with change direction 90*with passive rest 25'' between repetitions 3-4'min between set.
The parameters to be considered
- Increasing intensity (mainly for short intervals)
- Decreasing recovery time at fixed work interval
- Taking advantage of a passive recovery, especially in the all-out intensity
In conclusion, it can be said that high intensity training is the present and future of the methodology in football. In fact, several studies have shown that physiological adaptations and performance improvements (especially number and frequency of high intensity actions in the race) are relevant and influence discrimination between players.(Iaia ,2009 )
Αuthor :Pasquale D'Antonio (Preparatore Atletico Professionista ) Il Nuovo Calcio -Number 305
Δευτέρα 21 Μαΐου 2018
Congresso Internazionale :Training Load and Recovery in Football
Posted by
paulgotsis
at
6:47 μ.μ.
Training Load and Recovery in Football (Exchange Experiences and Opinions )
Date:28.05.2018 Nelson Mantela Forum Firenze Excellent organization, very good all the speakers, much better compared to previous years. I think the speakers who stood out were V.Di Salvo (National Team Italia ), A.Azzalin (Nantes Fc) ,S.Folletti (Juventus fc).
I will show you some slides from these speakers .
1.La Gestione dell'allenamento del calciatore -V.di Salvo
a.Analysing the Football Performance Objectives
b.Football Perfirmance priorities for Academy Football (U13-U18)
c.Periodization in a Proffesional Squad
d.Comparison Game-Training ,different plaeyr load,distance,metabolic power
2.Programmazione dell' allenamento in diversi campionati europei :dati e riflessioni sul controlo del carico (Andrea Azzalin -Preparatore Atletico Nantes fc )
a.2 different microcycles from Monaco and Leicester
b. Aerobic Metabolism in Soccer :Simulations and patterns of play
*Increased total distance during the game
*Correlated to RSA
*Reduction of the negative metabolic effects related to the anaerobic metabolism
*Able to maintain a good ratio between work/power outpout in the end of the match
3.Filosofia di lavoro e strategie di recupero prima squadra -S.Folletti
(Preparatore Atletico Juventus fc )
a.Recovery strategies of the First Team Juventus
b.Assessment Test (Vo2max Test,FMS Test,Strength Isom Test,Isokinetic Test )
c.Performance Test (Mognoni Test -Lactate Threshold,HIT Test ,CMJ Test,Test Agility)
d.Protocol for the players after the Game (24h-48h after the Game)
e.Different protocolls for the players who played 48h after the match.
f.Individual F.S.Training programms before the Training
Very good presentations, many common in their lectures and all very interesting.
Home Message
1.Aerobic Metabolim in Soccer = Simulations and patterns of play
2.Not only training with the ball but training and without ball (General+Specific Training) for the Aerobic Mechanism
3.Balance betwwen load and recovery ,in reducing injuries.
4.Internal Load +External load after each training.
5.Replicate in the Microcycle Season Training.
For further information:paulgotsis@yahoo.gr
Τρίτη 15 Σεπτεμβρίου 2015
Hamstring Injuries : Prevention - Rehabilitation Part 3
Posted by
paulgotsis
at
10:54 π.μ.
Shakhtar prevention hamstrings strengthening .
Medical Department of Fc Shakhtar Donetsk
Hamstrings Work
The chapters include this video is :
a.General Hamstring and Gluteus Exercises
b.Eccentric Work
c.Elastic Work
d.Hamstring with Swiss ball
e.Exercises on Plint
f.Flexion with control (Movement Preparation )
g.Dynamic Exercises
I post this video on the 3rd of this research for the prevention of muscle injuries to the hamstrings because I find a complete and comprehensive video that can help every football team Fitness Coach.
I want to say something to help all players and Conditioning Trainers in Soccer .Give great weight to the use of eccentric exercises to strengthening and prevent muscle injuries on the Hamstrings, this is the key.(Paul Gotsis ,Soccer Conditioning Trainer in Soccer Teams )
Πέμπτη 10 Σεπτεμβρίου 2015
Hamstring Injuries : Prevention-Rehabilitation Part 2
Posted by
paulgotsis
at
4:06 μ.μ.
Date:19.11.2010
Useful exercises for Hamstring Prevention and Rehabilitation. I propose these exercises which the most of them I follow in my teams.Are exercises you can utilize in a personal programm or in a squad programm.Don't forget that ,the most commonly injury is the hamstring injury and if yoy like to decrease or to avoid these is important to put everyday one personal prevention programm for all the players and specific for the players who have problems (injuries) on the past in these muscles.
Paul Gotsis ,Soccer Conditioning Specialist
Τρίτη 8 Σεπτεμβρίου 2015
Hamstring Injuries : Prevention - Rehabilitation Part 1
Posted by
paulgotsis
at
2:38 μ.μ.
Hamstring Strain Exercises
The following strengthening exercises for the rehabilitation of hamstring injuries should be done progressively as part of our hamstring strain rehab program.
Hamstring rehabilitation exercises
The following is for information purposes only. We recommend seeking professional advice. Below are a number of progressively more difficult hamstring exercises. They should always be done pain free. Where you start and how fast you progress will depend on how bad your injury is and how long ago it was injured.Isometric contractions
Standing knee flexion
Hamstring catches
This should be done pain free both during, afterwards as well as the next day. A little bit of natural muscle soreness the following day is OK but if it is uncomfortable then take a step back. Again begin with 1 set of 10 reps and build up each day to 3 sets of 15 reps. An ankle weight can be used to increase the load on the muscle.
Bridge exercises
Single leg bridges are done in the same way ensuring you squeeze the gluteal muscles and aim to maintain a straight line from the shoulder on the ground to the knee at the top point of the exercise. Again, begin with 3 x 8 reps and build up.
Seated hamstring curl
Single leg hip extensions
Single leg ball pick up
The athlete places on foot in front of the other and bends down to pick up the medicine ball. They then repeat the movement to put the ball back down. Repeat this 5 to 10 times.
Lunge with ball
Good mornings
Norwegion leg curl
Virtual Sports Injury Clinic
Παρασκευή 14 Μαρτίου 2014
Il Functional Training come metodologia di allenamento per la prevenzione e il miglioramento della performance atletica
Posted by
paulgotsis
at
5:25 μ.μ.
Il functional training
è una metodologia di allenamento che porta al globale condizionamento fisico del corpo umano col fine di raggiungere l'equilibrio di
un sistema dove tutti i singoli componenti interagiscono armonicamente fra loro
procurando il benessere psico – fisico al soggetto praticante.
Attraverso la
stabilizzazione della regione del CORE, ossia il centro funzionale del corpo,
approfondendo le caratteristiche di flessibilità, equilibrio e propriocezione,
è possibile oltre che a ricercare vantaggi preventivi per tutta la regione
lombo – pelvica, anche ricercare vantaggi sulla produzione di ipertrofia
muscolare con annesso incremento della capacità di forza.
Con il termine ipertrofia muscolare si intende l'aumento del volume del muscolo, dovuto ad
un conseguente aumento di volume degli elementi che lo compongono: fibre,
miofibrille, tessuto connettivo, proteine contrattili, ecc…. L'ipertrofia
muscolare è il risultato, appunto, sia dell'aumento del volume che del numero
delle miofibrille, sia dello sviluppo degli involucri muscolari del tessuto
connettivo, sia dell'aumento della vascolarizzazione sanguigna e all'aumento
del numero di fibre. L'ipertrofia muscolare è favorita dalla forza ipertrofica
che nel functional training non è un vero e proprio punto di arrivo, perché ne
limiterebbe le capacità fisiche e atletiche del soggetto, ma comunque rientra
nei possibili benefici ottenibili.
La forza ipertrofica è
caratterizzata dall'esecuzione degli esercizi di base per un numero di
ripetizioni che si aggirano intorno alle 6/15 in quanto attraverso una
intensità di sforzo ed una durata corrispondente a questo parametro, a causa di
particolari condizioni biochimiche che si generano nell'organismo, si stimola
al meglio la sintesi proteica e di conseguenza anche l'ipertrofia muscolare.
Si parla di numero di
ripetizioni di 6/15 perché sono quelle che favoriscono la sintesi proteica, in
quanto la durata della tensione muscolare rientra tra i 20 secondi e il minuto.
Attraverso questo tipo di lavoro, inoltre, c'è anche una notevole attivazione
di actina e miosina.
Con il functional
training, quindi, le possibilità di aumentare e sviluppare la massa muscolare
avviene utilizzando le medesime ripetizioni per ogni esercizio di base.
Generalmente nel lavoro funzionale l'esercizio di base è lo squat, che
privilegia lo sviluppo dei muscoli delle gambe senza tralasciare i muscoli
stabilizzatori che sono i maggiori produttori di forza nell'individuo.
Grazie al
condizionamento atletico, quindi, l'esecuzione di un allenamento è mirato a
condizionare le capacità atletiche del soggetto praticante ed è perciò
possibile eseguire determinati movimenti attraverso caratteristiche specifiche
col fine di aumentare la forza. È impensabile credere che la forza aumenti
semplicemente allenandosi con macchine isotoniche che vanno ad isolare i
determinati distretti muscolari, ma bisogna affermare che il soggetto si rende
più forte se è capace di utilizzare nei movimenti il maggior numero di muscoli possibili, facendoli lavorare in modo sinergico.
Per aumentare la forza
bisogna utilizzare esercizi in grado di infierire e rendere efficiente il
lavoro di diverse catene cinetiche all'unisono.
Per condizionare il corpo umano bisogna migliorare le diverse capacità fisiche e atletiche. Oltre alle capacità motorie coordinative e condizionali sopracitate, per il raggiungere un discreto condizionamento motorio è indispensabile analizzare le capacità cardiovascolari.
Per condizionare il corpo umano bisogna migliorare le diverse capacità fisiche e atletiche. Oltre alle capacità motorie coordinative e condizionali sopracitate, per il raggiungere un discreto condizionamento motorio è indispensabile analizzare le capacità cardiovascolari.
La principale funzione
delle capacità cardiovascolari è quella di fornire sangue e ossigeno ai
muscoli. L'apparato respiratorio, il sistema cardiocircolatorio e l'apparato
muscolare sono i fautori di questa capacità. Per la produzione di energia da
utilizzare per qualsiasi tipo di movimento è necessaria la fornitura di sangue
ai muscoli.
Il functional training
deve essere in grado di ottimizzare al meglio la capacità cardiovascolare così da sostenere l'atleta un forte sostegno negli
sforzi maggiori in tempi medio – lunghi. Per migliorare la capacità
cardiovascolare si lavora con attività aerobiche a bassa intensità. Partendo
dal presupposto che la frequenza cardiaca massima del soggetto si riesce a
calcolare grazie alla formula (220 - età del soggetto) si può andare definire
qualsiasi tipo di intensità lavorativa. Generalmente per un lavoro a bassa
intensità la percentuale di carico sarà più o meno al 65% della frequenza cardiaca massima con una durata minima della seduta di 40 minuti.
Per condizionare le
capacità cardiovascolari si può anche utilizzare il metodo dell'interval training, cioè lavoro ad alta intensità intervallata. Alternare
esercizi dove l'esecuzione delle serie e delle ripetute sarà al massimo di 2 -
3 minuti per poi passare all'attività aerobica per altri 2 - 3 minuti e poi
ripetere il giro.
Per condizionarsi al
meglio eseguendo esercizi di forza, senza eseguire le classiche attività aerobiche (corsa,
bici) è il caso di dedicarsi a movimenti o esercizi multiarticolari che
reclutano il maggior numero di gruppi muscolari (squat) così da costringere il
cuore a lavorare ad alto ritmo, fornendo più sangue ai vari distretti muscolari
coinvolti.
Il condizionamento
motorio avviene anche grazie all'allenamento attraverso la ricerca della potenza aerobica (VO2Max). Essa indica la quantità di ossigeno
utilizzabile in un determinato tempo.
In senso stretto il VO2Max può essere sostenuto al massimo per una decina di minuti (Prampero, 1987). Attraverso l'allenamento il suo valore può essere incrementato dal 10 al 25 %. Nel corso di un attività fisica coinvolgente le grandi masse muscolari, essa è di intensità progressivamente crescente ed è protratta fino all'esaurimento. Il modo più efficace per migliorare la VO2Max è quello di svolgere attività anaerobiche così da far creare la supercompensazione dovuta al protrarsi oltre il limite ed entrare inevitabilmente quindi, nei processi anaerobici.
In senso stretto il VO2Max può essere sostenuto al massimo per una decina di minuti (Prampero, 1987). Attraverso l'allenamento il suo valore può essere incrementato dal 10 al 25 %. Nel corso di un attività fisica coinvolgente le grandi masse muscolari, essa è di intensità progressivamente crescente ed è protratta fino all'esaurimento. Il modo più efficace per migliorare la VO2Max è quello di svolgere attività anaerobiche così da far creare la supercompensazione dovuta al protrarsi oltre il limite ed entrare inevitabilmente quindi, nei processi anaerobici.
Per condizionare al
meglio questa capacità è utile applicarsi con esercizi multiarticolari (scatti di corsa, skip, scale) attraverso eccessive
ripetizioni, anche senza intervalli di recupero, in modo tale da tenere sempre
alto il livello di lattato.
Anche l'allenamento sulla capacità di lavoro è utile per il raggiungimento del condizionamento
motorio. La capacità di lavoro indica l'esecuzione di movimenti faticosi,
perlopiù esercizi di forza, per un lungo periodo di tempo. Può essere
paragonata alla forza resistente, dato che consente al corpo di lavorare più o
meno alla stessa intensità per lungo tempo. In questo caso avviene un
condizionamento muscolare e cardiovascolare.
Il condizionamento muscolare avviene
grazie ai muscoli che devono riuscire a svolgere gesti di forza per un tempo
prolungato, mente il condizionamento è anche cardiovascolare,
perché si intende, appunto, un tempo di lavoro alquanto lungo.
L'allenamento funzionale, inoltre, deve migliorare l'agilità dell'atleta,
capacità che consente di effettuare con disinvoltura qualsiasi tipo di
movimento, semplice o complesso, in qualsiasi luogo e situazione a velocità
elevata. L'agilità è un elemento fondamentale nella vita quotidiana perché
permette al soggetto di svolgere movimenti veloci, controllando il corpo
seppure l'esecuzione viene eseguita in scioltezza e disinvoltura. Il
miglioramento dell'agilità attraverso l'allenamento funzionale è possibile
ottenerlo attraverso esecuzioni e ripetute
di movimenti molto articolati e creativi, molto spesso a limite della forza di gravità (capriole
senza mani, salti, ruote con una mano, anche in successione fra loro).
Durante qualsiasi
esecuzione di qualsiasi movimento, mediante una seduta di functional training,
per agire efficacemente sull'ottenimento dell'ipertrofia muscolare, la velocità
e la forza sono in continuo rapporto e confronto.
Quando il carico sarà
maggiore l'esecuzione non sarà veloce, ma il soggetto dovrà agire con gran
forza per vincere il sopra citato carico esterno, a differenza di quando il carico
sarà minore e l'esecuzione sarà più veloce senza necessitare di troppa forza.
Queste due capacità nella loro sinergia sono determinanti per il raggiungimento
degli obiettivi in qualsiasi prestazione, quindi, si può affermare che sono
imprescindibili l'una dall'altra. Esse in ogni seduta di allenamento devono
essere condizionate per la buona riuscita della performance e periodicamente
devono essere valutate per verificarne i miglioramenti e la globale esecuzione
dei movimenti in modo rapido, esplosivo e coordinato.
Titolo
della tesi: Il
Functional Training come metodologia di allenamento per la prevenzione e il
miglioramento della performance atletica
Anno accademico: 2011 - 2012
Università: Università degli studi di Foggia
Facoltà: Dipartimento di Medicina Clinica Sperimentale Corso di Laurea in Scienze delle Attività Motorie e Sportive
Relatore: Professor Pierluigi De Pascalis allenamentofunzionale.biz
Anno accademico: 2011 - 2012
Università: Università degli studi di Foggia
Facoltà: Dipartimento di Medicina Clinica Sperimentale Corso di Laurea in Scienze delle Attività Motorie e Sportive
Relatore: Professor Pierluigi De Pascalis allenamentofunzionale.biz
Παρασκευή 4 Οκτωβρίου 2013
Individual Preparation before the Training True or False
Posted by
paulgotsis
at
4:35 μ.μ.
Trainings today both in Greece and in Europe are more general in nature.The duration of the training range between 1.15'-1.30' .Ιt's enough for the players to have improvement only with the daily workouts.Finaly is True or False to make someone a Pre-warm up Training in the Gym before the normal training ?
My opinion is that the players MUST make a pre warm -up traing 3-4 times per week.I have an excellent experience in my previous squad Skoda Xanthi Fc where I established this process.Initially the players didn't like to follow this and were hesitant.(The process was all the players except the injured players 45'min- 1 hour before in the Gym .But after 4-5 months they understοοd my philosophie.
Every player had an individual Programm in relationship with his deficiencies.
Τhe exercises are for all the muscles.(Abs-Planks-Lunges -etc).The target of these Individual Programms are:
1.Better entrance in the Warm up of the Squad.
2.Ιmprove muscle imbalances
3.Injury Prevention (Enough Prioproceptive Exercises)
4.Core Stability for the whole Trunk
5.Energise the testosterone
6.Better Cocentration inside in the Training
The results were incredible.The improvement high.Enough players and when after left of the sguad continue this work because understand the results of this work.They trusted my work because they had higher performance without Injuries. I SUGGEST IT BUT WITH PROGRAMMES AND MEASURES.
 Italiana Lingua
Italiana Lingua
2.Migliorare squilibri muscolari.
3.Infortuni preventiva (Propriocettiva esercizi).
4.Core Stabilization per tutto il tronco.
5.Accendere le testosterone nel muscoli dei giocatori.
6.Migliore concentrazione nel allenamento.
I risultati sono stati altamente e estrenamente.Le miglioramento grande.Alcuni giocatori ancora lasciato con la squadra hanno continuato questo lavoro anche perche che si fida di me.Αbbiano fiducia perche hanno visto i risultati,alta efficienza senza infortuni. IO PROPPORE QUESTO LAVORO MA SEMPRE CON PROGRAMMA E MISURA.
http://youtu.be/yxcmdHsebiE
My opinion is that the players MUST make a pre warm -up traing 3-4 times per week.I have an excellent experience in my previous squad Skoda Xanthi Fc where I established this process.Initially the players didn't like to follow this and were hesitant.(The process was all the players except the injured players 45'min- 1 hour before in the Gym .But after 4-5 months they understοοd my philosophie.
Every player had an individual Programm in relationship with his deficiencies.
Τhe exercises are for all the muscles.(Abs-Planks-Lunges -etc).The target of these Individual Programms are:
1.Better entrance in the Warm up of the Squad.
2.Ιmprove muscle imbalances
3.Injury Prevention (Enough Prioproceptive Exercises)
4.Core Stability for the whole Trunk
5.Energise the testosterone
6.Better Cocentration inside in the Training
The results were incredible.The improvement high.Enough players and when after left of the sguad continue this work because understand the results of this work.They trusted my work because they had higher performance without Injuries. I SUGGEST IT BUT WITH PROGRAMMES AND MEASURES.
PREPARAZIONE INDIVIDUALE PRIMA L'ALLENAMENTO GIUSTO O SBAGLIATO ?
Allenamenti oggi sia in Grecia sia in Europa hanno simile modulo di lavoro (piu genere).Durata le allenamento e 1.15'min -1.30'min .E sufficiente per i giocatori che hanno un miglioramento solo con quotidiano allenamenti.
Ιnfine e giusto o sbagliato si fa pre-riscaldamento in palestra prima di normale allenamenti?
A mio avisso i giocatori devono fare un pre-riscaldamento in palestra 3-4 volte per settimana .Ho avvuto un notevole esperienza la mia ultima squadra -Skoda Xanthi fc Super League Grecia-devo stabilito questa processο.La procedura era tutti i giocatori sono 45'-1 ora prima di allenamento in palestra ,oltre a gli infortunati.Come principio i giocatori erano esitanti .Dopo 4-5 mesi capito la mia filosofia.Ogni giocatore ha un specifiche programma rispeto le suoi diffeti.Le esercitazioni in palestra sono stati (Abdominale-Affondi-Squats-etc).L'obiettivo di questi esercizi e' :
1.Migliore entrata nel primis riscaldamento.2.Migliorare squilibri muscolari.
3.Infortuni preventiva (Propriocettiva esercizi).
4.Core Stabilization per tutto il tronco.
5.Accendere le testosterone nel muscoli dei giocatori.
6.Migliore concentrazione nel allenamento.
I risultati sono stati altamente e estrenamente.Le miglioramento grande.Alcuni giocatori ancora lasciato con la squadra hanno continuato questo lavoro anche perche che si fida di me.Αbbiano fiducia perche hanno visto i risultati,alta efficienza senza infortuni. IO PROPPORE QUESTO LAVORO MA SEMPRE CON PROGRAMMA E MISURA.
Internazionale Fc players make Pre-warm up before the Training.
Fitness Coach-Preparatore Atletico Proffesionista
Paul Gotsis
 |
Εγγραφή σε:
Αναρτήσεις (Atom)